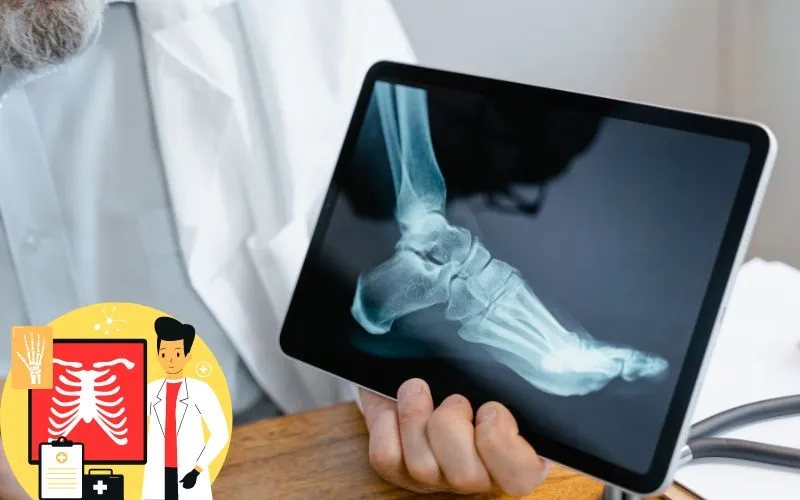
An X-ray is a type of imaging diagnose technique that captures images of bones and soft tissues. X-rays produce images with safe levels of radiation. Doctors may use the photos to diagnose and arrange therapies for various diseases. Typically, doctors utilise X-ray tests to assess fractured bones, dislocated joints, and other bone ailments.
How X-Rays Work: A Simple Explanation
X-rays use a small amount of radiation to capture images of your bones and tissues. The machine sends beams through your body, creating images doctors view on a screen.
This technique passes X-ray beams through the body, where denser materials like bones block the rays, creating clear pictures of internal structures.
X-rays are safe when used responsibly. Doctors minimise risks by using the lowest radiation possible and shielding sensitive areas. Most patients experience no discomfort, making X-rays a reliable diagnostic tool in Dwarka.
Uses of X-ray
These are the most common uses of an X-ray in Dwarka, Delhi:
Diagnosing bone injuries and tumours
X-rays can help diagnose bone injuries and tumours, but doctors typically require additional tests to confirm a diagnosis. X-rays can show evidence of bone tumours, which can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Bone cancer can appear on an X-ray in many ways, including:
- Ragged appearance
- Less solid appearance
- Holes, Layered appearance
- Thin appearance
- Perforated appearance.
However, X-rays may not be able to immediately show subtle fractures, including those in skeletally immature children and some stress fractures. If symptoms of a fracture persist, follow-up X-rays may show a fracture due to loss of bone around the fracture site during the healing process.
Identifying the cause of symptoms like pain and swelling
An X-ray can help identify the cause of persistent swelling, such as a bone fracture or fluid around a joint. X-rays can also show changes in soft tissues that may contribute to inflammation. However, X-rays can’t directly visualise inflammation, but they can show changes in bones and tissues that suggest an ongoing inflammatory process.
Looking for foreign objects in the body
A doctor can diagnose a foreign object in the body by taking a history from the patient or a family member and performing a physical exam. X-rays can detect foreign bodies that are denser than soft tissue, such as metal, glass, and gravel because they attenuate more rays and appear in greater contrast to the surrounding areas.
Looking for structural problems in bones, joints, or soft tissues
X-rays are a quick and painless imaging test that can help detect structural problems in bones, joints, and teeth. X-rays are most useful for detecting bone abnormalities, such as:
- Fractures
- Abnormal bone positions
- Bone diseases, like osteoarthritis
- Tumors
- Injuries
- Infections
- Deformities, such as developmental dysplasia of the hip
- Arthritis.
X-rays can also be used to plan surgery or to check the position of a prosthesis after an operation. However, X-rays do not show soft tissues such as muscles, bursae, ligaments, tendons, or nerves.
Who Needs an X-Ray?
An X-ray is important for diagnosing injuries, illnesses, or abnormalities in bones and soft tissues. Doctors in Dwarka recommend X-rays when symptoms or injuries require detailed imaging for accurate diagnosis. Here are a few scenarios explaining why some patients may require an X-ray –
- People with fractures or broken bones need X-rays for proper diagnosis.
- Patients with joint pain or swelling require X-rays to identify the cause.
- X-rays help in detecting tumours or abnormal growths in bones.
- Doctors use X-rays to examine persistent back pain or spinal issues.
- Pregnant women may need chest X-rays for lung or rib issues with precautions.
- Athletes with sports injuries often undergo X-rays to assess the damage.
- Routine screenings, like mammograms, use X-rays for early cancer detection.
Planning treatment
X-rays lab in dwarka are a valuable medical tool that helps doctors plan and evaluate treatments. X-rays can also help doctors monitor the progress of bone-related conditions, such as fractures, and evaluate the success of surgical interventions. X-rays are the most commonly used form of imaging for diagnostic purposes. They are often the first step in helping doctors understand a patient’s situation and plan the best way to treat it. X-rays can also help doctors guide medical personnel as they insert catheters, stents, or other devices inside the body, treat tumours, or remove blood clots or other blockages.

Providing routine screenings for cancer and other diseases
X-rays can show changes in bones caused by cancer. X-rays are safe for most people because they produce a small amount of radiation that doesn’t cause discomfort. Mammography is the specialised X-ray technique used in the early detection of breast cancer. Regular mammograms are recommended for women over a certain age or those with a higher risk of breast cancer to catch the disease at an early, more treatable stage.
How to prepare for an X-ray?
Different types of X-rays require different preparations. In general, you should:
- Inform the hospital: Let the hospital know if you are pregnant.
- Wear loose clothing: Wear loose, comfortable clothing or change into a gown before the X-ray.
- Remove metal objects: Remove jewellery, eyeglasses, hairpins, hearing aids, and other metal objects.
- Avoid lotions and perfume: Avoid using lotions, creams, or perfume.
- Stop eating and drinking: For GI X-rays, stop eating and drinking several hours beforehand.
- Arrive early: Arrive at least 15 minutes before your appointment.
- Leave valuables at home: Leave your valuables at home or in your hospital room.
- Bring identification: Verify your identification and the exam requested.
During the X-ray, your doctor move your torso or limbs around and urge you to remain motionless. You may need to hold your breath for a few seconds to ensure that the visuals are clear. Even though X-rays employ radiation (which can cause cancer and other health issues), the danger of radiation overexposure is negligible. Some X-rays emit higher levels of radiation than others. Overall, X-rays are both safe and helpful for people of all ages.
X-rays help your doctor evaluate your health, make an accurate diagnosis, and plan treatments. Before getting an X-ray, notify your doctor if you are pregnant. X-rays are a safe and effective tool that doctors use to help patients feel better and remain healthy. Reach out to Doctor’s Hub Super Speciality Clinic for various tests and screenings.